How to Change Font Style in CSS –Typography plays a critical role in web design. Whether you want your text to stand out, look elegant, or be easily readable, CSS offers multiple ways to control the appearance of text on a webpage. From bold headlines to elegant body text, fonts are an essential aspect of your website’s visual language. So, exactly How to Change Font Style in CSS?
Understanding Font-Family Property
The font-family property is your gateway to choosing different fonts for your web pages. It defines the typeface of your text and allows for a list of fallback fonts in case the primary font isn’t available on the user’s device.
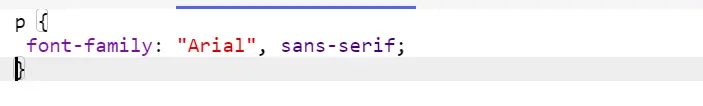
p {
font-family: "Arial", sans-serif;
}
Explanation:
The browser will first try to render Arial. If it’s unavailable, it will use the generic sans-serif font. You can list multiple fallback fonts, separated by commas, to ensure better cross-browser compatibility.
Customizing Font-Style in CSS
The font-style property lets you control whether your text is italicized, oblique, or normal. This property is perfect for emphasizing certain parts of your content, such as quotations or product descriptions.
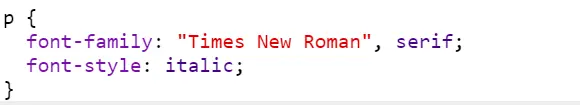
p {
font-family: "Times New Roman", serif;
font-style: italic;
}
Explanation:
This example italicizes the text. The browser first tries Times New Roman, and if it is unavailable, it defaults to a serif font. Italics are commonly used for quotes or to highlight specific words.
Adjusting Font Weight for Impact
The font-weight property is another essential tool that lets you control how bold your text appears. It ranges from lighter (100) to bolder (900), but using values like bold and normal is more common in everyday use.
p {
font-family: "Arial", sans-serif;
font-weight: bold;
}
Explanation:
In this case, the text will appear bold. The font-weight property is useful for emphasizing headings or key terms within a body of text.
Combining Font-Related Properties
The font shorthand property allows you to combine multiple font-related properties in one line. This can include font-size, font-family, font-weight, font-style, and even line-height.
p {
font: bold italic 18px/1.5 "Times New Roman", serif;
}
Explanation: How to Change Font Style in CSS
This CSS rule sets the font to bold and italic with a size of 18px, a line height of 1.5, and uses Times New Roman with a fallback of serif. This shorthand property makes it easier to manage typography while keeping your CSS clean.
Using Custom Fonts with @font-face
If the built-in fonts aren’t cutting, you can easily import custom fonts from sources like Google Fonts or even use your own with @font-face. This expands your design options and helps create unique web experiences.
@font-face {
font-family: "MyCustomFont";
src: url("mycustomfont.woff2") format("woff2");
}
p {
font-family: "MyCustomFont", sans-serif;
}
Example Code of Font Style in CSS
p {
font-family: "Arial", sans-serif;
font-style: italic;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 18px;
}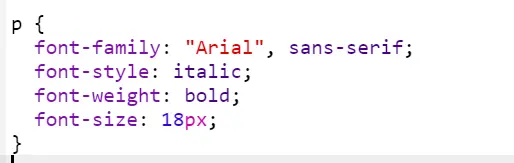
In this case, we combine several properties to achieve bold, italic text using Arial as the primary font. If Arial isn’t available, the browser falls back to the default sans-serif font.
Table for Font Style in CSS Property
| Property | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
| font-family | Specifies the typeface | “Arial”, “Times”, etc. |
| font-style | Controls italics or obliques | normal, italic, oblique |
| font-weight | Adjusts the boldness | normal, bold, 100–900 |
| font-size | Adjusts the size of the text | Any valid CSS size unit |
| line-height | Sets the space between lines | Any valid CSS size unit |
| font | Combines multiple font settings | Various combinations |
Browser Compatibility and Fallbacks: Font Style in CSS
Fonts might not render the same across all browsers. That’s where fallback fonts come in handy. Always list multiple fonts so that if one fails to load, another one takes its place.
Why Font Styles Matter in Web Design
Fonts are more than just decoration—they set the tone of your content. For example, serif fonts are often associated with tradition, while sans-serif fonts appear more modern and clean. The right font can make your content easier to read, more memorable, and more engaging.
Optimizing Font Styles for SEO
Search engines pay attention to readability, and if users have a hard time reading your text, they’re likely to leave the page quickly. Well-chosen font styles ensure better user engagement, which can indirectly affect your SEO by improving dwell time.
FAQs
Can I use multiple fonts in one CSS rule?
Yes, you can specify multiple fonts using the font-family property as fallbacks in case the browser doesn’t support the first one.
What is the default font style in CSS?
The default font style is usually normal, but this depends on the browser.
How can I load custom fonts into my CSS?
You can use the @font-face rule or import them from services like Google Fonts.
How do I make text bold without changing font-family?
Use the font-weight property and set it to bold.
Can I animate font styles in CSS?
Yes, you can animate font styles.