State and Props in React- React is one of the most popular JavaScript libraries for building interactive user interfaces. When working with React components, two fundamental concepts are crucial State and Props. These concepts help manage data and enable communication between components, ensuring a dynamic and responsive UI. In this article, we’ll explore state and props in React, their differences, and how to use them efficiently in your applications.
Introduction to React Components
React applications are built using components, which are reusable building blocks of UI. These components can be either functional or class-based. To make components dynamic and interactive, we use State and Props in React.
- Props (Properties): Used to pass data from a parent component to a child component.
- State: Used to manage dynamic data that changes over time within a component.
Let’s dive deeper into each concept.
What are Props in React?
Props (short for “properties”) are read-only and are used to pass data from a parent component to a child component. Props help make components reusable and dynamic by providing different inputs.
How to Use Props in React
To use props, you pass them as attributes when rendering a child component.
Example of Props in React
import React from 'react';
const Greeting = (props) => {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}!</h1>;
};
const App = () => {
return <Greeting name="John" />;
};
export default App;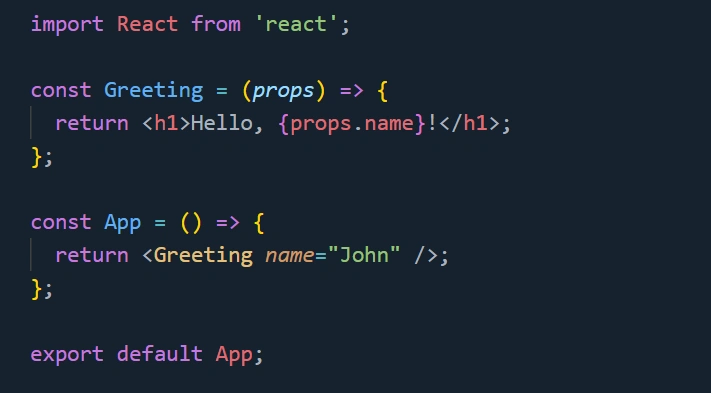
Here, name is passed as a prop to the Greeting component.
What is State in React?
State is a built-in React object used to manage a component’s internal data. Unlike props, state is mutable, meaning it can change over time.
Managing State in React
State is initialized in a component and updated using the useState hook (for functional components) or setState (for class-based components).
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const Counter = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>Count: {count}</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Increase</button>
</div>
);
};
export default Counter;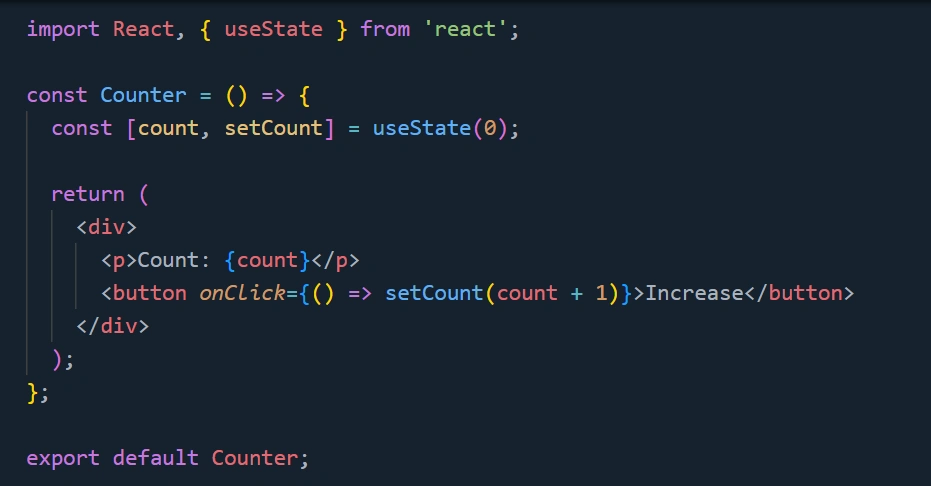
Here, count is a state variable that updates when the button is clicked.
Key Differences Between State and Props in React
| Feature | State | Props |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internal data storage for a component. | Read-only data passed from parent to child. |
| Mutability | Mutable (can be updated using setState or useState). | Immutable (cannot be modified by the child component). |
| Ownership | Managed within the component. | Controlled by the parent component. |
| Usage | Used for managing dynamic data and UI behavior. | Used for passing data and event handlers to child components. |
| Re-rendering | Causes the component to re-render when updated. | Triggers re-render if new props are received. |
| Access | Available only within the component that owns it. | Passed down from parent to child and accessed via props. |
Using Props and State Together
You can combine props and state to create powerful, interactive components. For example:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const DisplayCounter = ({ count }) => {
return <h2>Current Count: {count}</h2>;
};
const CounterApp = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<DisplayCounter count={count} />
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Increase</button>
</div>
);
};
export default CounterApp;
Here, the count is stored in the state and passed as a prop to DisplayCounter.
Best Practices for Using State and Props in React
- Use Props for Static Data: Props should be used for data that doesn’t change, like component configurations.
- Use State for Dynamic Data: State should be used for data that changes based on user actions.
- Avoid Modifying Props: Since props are read-only, never try to modify them in a child component.
- Lift State Up: When multiple components need access to the same state, store it in the closest common parent.
Conclusion
Understanding state and props in React is essential for building interactive applications. While props allow data to be passed between components, state enables dynamic behavior. By using them effectively, you can create highly modular and reusable React components.
FAQs
Can a child component modify its props?
No, props are immutable and cannot be changed by the child component.
When should I use state instead of props?
Use state when the data needs to change within a component; use props to pass data that remains constant.
How does updating state affect React components?
When state updates, the component re-renders to reflect the new data.
Can I use props in class components?
Yes, in class components, props are accessed using this.props.
What is the best way to manage global state in React?
For global state management, use Context API, Redux, or Zustand.