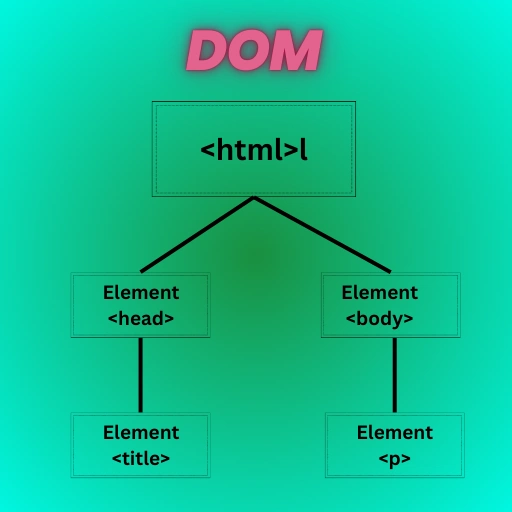
What are DOM Elements in JavaScript: The Document Object Model, or DOM, is the backbone of every modern web page. When a web page loads in your browser, the HTML document transforms into a structured tree-like representation known as the DOM. Think of it as a map that links all the elements on your page.
How the DOM Represents HTML
Every HTML tag—like <div>, <p>, or <h1>—becomes a node in this DOM tree. These nodes are JavaScript objects that you can manipulate, whether it’s changing the text inside a paragraph or hiding an image.
The Importance of the DOM in Web Development
The DOM bridges the gap between HTML and JavaScript, allowing you to create interactive and dynamic web pages. Without it, your web applications would be static and lifeless.
Key Features of DOM Elements in JavaScript
HTML Tags as Nodes in the DOM
In the DOM, every HTML tag is represented as a node. For instance, the tag becomes a parent node, while nested elements like <div> or <p> become child nodes.
DOM Elements as JavaScript Objects
Each DOM element is an object with properties and methods you can use to interact with it. For example, a <p> element has properties like textContent to get or set its text.
| What is DOM Manipulation in JavaScript?(Easy Tips) |
| How to Generate HTML Form Design Examples with Code(5+) |
Accessing DOM Elements in JavaScript
Accessing DOM elements is straightforward with JavaScript. Let’s dive into some popular methods: document.getElementById() This method selects an element by its unique ID.
const element = document.getElementById('header');
console.log(element.textContent); // Outputs the text inside the element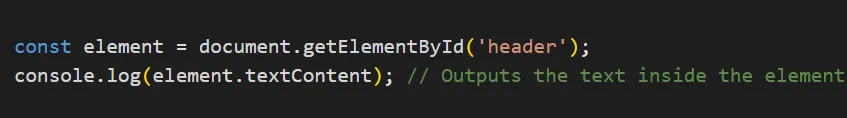
document.getElementsByClassName()
Selects all elements with a specific class name.
const items = document.getElementsByClassName('item');
console.log(items[0].textContent); // Accesses the first item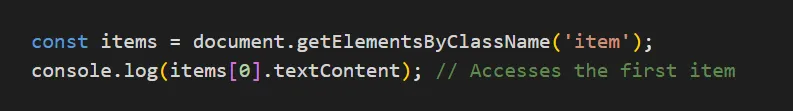
document.getElementsByTagName()
Target elements by their tag name, like <div> or <p>
const paragraphs = document.getElementsByTagName('p');
console.log(paragraphs.length); // Outputs the number of paragraphs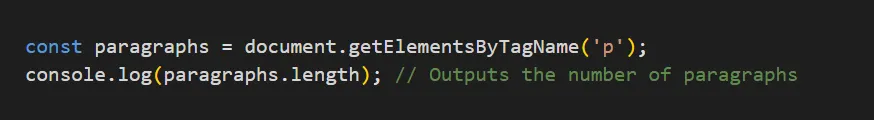
document.querySelector()
Selects the first element matching a CSS selector.
const firstButton = document.querySelector('.button');
firstButton.style.color = 'red';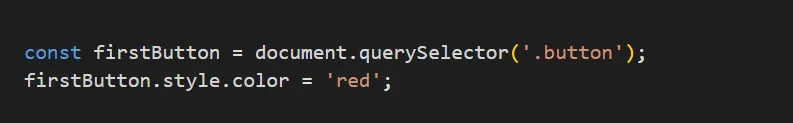
document.querySelectorAll()
Fetches all elements matching a CSS selector.
const buttons = document.querySelectorAll('.button');
buttons.forEach(button => button.style.color = 'blue');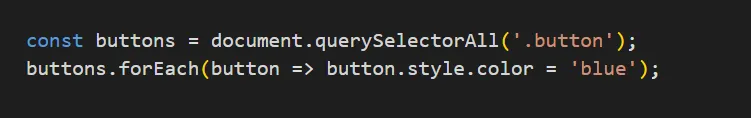
Properties and Methods of DOM Elements
Common Properties
innerHTML:Gets or sets HTML content.textContent:Gets or sets plain text.style:Accesses inline styles.
Using Methods
setAttribute():Adds or modifies an attribute.addEventListener():Adds event listeners to elements.
Creating and Removing DOM Elements
Creating New Elements
const newDiv = document.createElement('div');
newDiv.textContent = 'I am a new div!';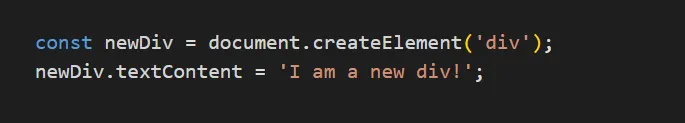
Appending Elements to the DOM
document.body.appendChild(newDiv);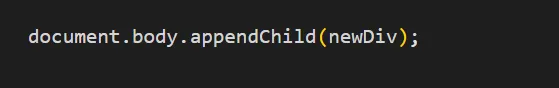
Removing Elements from the DOM
document.body.removeChild(newDiv);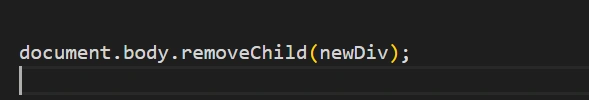
Advantages of Using DOM Elements in JavaScript
Enhancing User Interaction
DOM manipulation allows you to create a richer user experience, like opening modals or validating forms.
Making Web Pages Dynamic
With the DOM, your pages can update content dynamically, responding to user actions without reloading.
FAQs
It’s a structure representing the HTML document that allows JavaScript to interact with the page.
Use document.getElementById('id').
innerHTML includes HTML tags; textContent includes plain text only.
Yes, using document.createElement().
It enables dynamic and interactive web pages.