What is the Overflow Property in CSS – The overflow property in CSS determines how content is handled when it overflows the boundaries of its container. By default, content that exceeds the container’s size may still be visible, but this behavior can be controlled using different values for the overflow property. The values allow you to manage how excess content is displayed, whether it’s visible, hidden, or scrollable.
Let’s explore what is overflow property is in CSS with examples and discuss each aspect in detail.
What is Overflow Property in CSS: Syntax and Usage
The basic syntax of the overflow property is as follows:
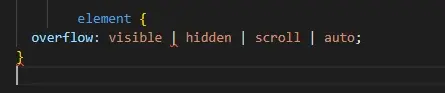
This property can be applied to any block-level container element to handle overflowing content. The behavior changes based on the value assigned to the overflow property, as described below:
visible: Content is allowed to overflow the container and will be visible.hidden: Overflowed content is clipped, and only the content within the container’s box is shown.scroll: Scrollbars appear regardless of whether the content overflows.auto: Scrollbars appear only if the content overflows the box.
Table of Contents
Code Example: Overflow with Div Element
Consider the following CSS code: Overflow Property in CSS
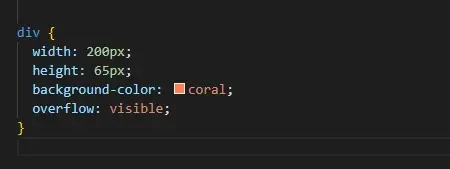
In this complete example, the div container is set to a width of 200px and a height of 65px. The overflow: visible; value allows any overflowing content to appear outside the defined box, with no clipping or scrollbars. Here’s what each part of the code does:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| width: 200px; | Sets the width of the container to 200 pixels. |
height: 65px; | Sets the height of the container to 65 pixels. |
| background-color | Changes the background color to coral. |
| overflow: visible | Content beyond the defined box is still visible. |
How does it work: Overflow Property in CSS?
If the text inside the div exceeds the defined width or height, it will overflow and remain visible outside the boundaries of the container, as the overflow property is set to visible.
Overflow Property Values Explained
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| visible | Content overflows and is visible outside the element’s container. (Default) |
| hidden | Overflowing content is clipped and will not be visible outside the container. |
| scroll | Scrollbars appear regardless of whether the content overflows or not. |
| auto | Scrollbars appear only if the content exceeds the container’s dimensions. |

What is the Overflow Property in CSS?
A: The visible value for the overflow property allows content that overflows the element’s box to remain visible outside of it. This is the default behavior for most elements.
What happens if I set overflow: hidden;?
A: When you set overflow: hidden;, any content that exceeds the defined box size will be clipped and not visible. This is useful when you want to enforce strict boundaries on content display.
What’s the 2 difference between overflow: scroll; and overflow: auto;?
A: With scroll, scrollbars will always appear regardless of whether content overflows. In contrast, auto adds scrollbars only when content actually exceeds the container’s size.
Can I use overflow for inline elements?
A: The overflow property typically applies to block-level containers like div. It does not work as expected with inline elements such as span.